Birth control not only helps women prevent unwanted pregnancies, but it also reduces the oh-so-painful symptoms and excess bleeding that most of us get during our time of the month.
But with all the benefits aside, there are also a few side effects to be wary of. Check out some of the most popular types of birth control and their risks below.
Keep in mind that whatever birth control you use, it’s important to talk to your gyno about the risks as well.
Birth control pills
There are so many different kinds of birth control pills with varying degrees of hormones — some only include progestin, while others have both progestin and estrogen. While progestin-only pills (aka “mini pills”) aren’t associated with causing significant side effects, you should still know that taking birth control pills can increase your blood pressure and cholesterol levels, which could impact your overall heart health. Typically, these increases aren’t severe enough for you to stop taking the pill, but in rare instances, they can have serious side effects including blood clots, tumors on the liver, heart attacks, and strokes.
Depo-Provera
Some minor symptoms women may experience after the depo shot include headaches, stomach pain, breast soreness, dizziness, nervousness, and weight gain. However, depo shots can also increase a woman’s risk for osteoporosis, which is why most doctors don’t recommend wearing one for more than two years. If you’re at a higher risk for osteoporosis (like an eating disorder or history of osteoporosis in your family), you may want to consider a different birth control method. Also, some women may have a delay in their return to fertility, so they may not want to get the depo shot if they plan on getting pregnant within the next year.
IUDs
The most common side effects of IUDs include soreness, cramping, back pain, discomfort, and irregular periods for about three to six months until the IUD has fully taken effect. Although rare, the IUD can also push through the uterine wall and require surgical removal while other women can experience an infection due to the presence of a foreign object in the uterus.
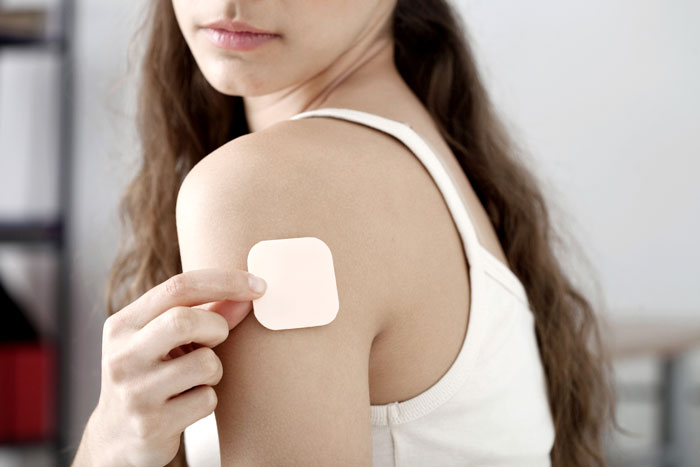
The patch
Just like with an IUD, there might be an adjustment period for your body to get used to the hormones in the patch. Side effects during this time can include sore breasts, nausea, bleeding between periods, and soreness, specifically where the patch is applied. Since the birth control patch contains estrogen, it increases the likelihood of some serious health problems including risks for breast cancer, blood clots, high blood pressure, and a heart attack. This is why most doctors don’t recommend the patch to women older than 35 or those who smoke because these factors increase your risk of adverse side effects.
xx, The FabFitFun Team